Today is the Spring Equinox of 2015. An equinox occurs when the Sun shines directly over the earth's equator. This makes night and day almost equal in length There are two equinoxes every year, in March and September.The Spring equinox occurs on the 19th, 20th, and 21st of March, the Fall equinox on September 22nd, 23rd and 24th.
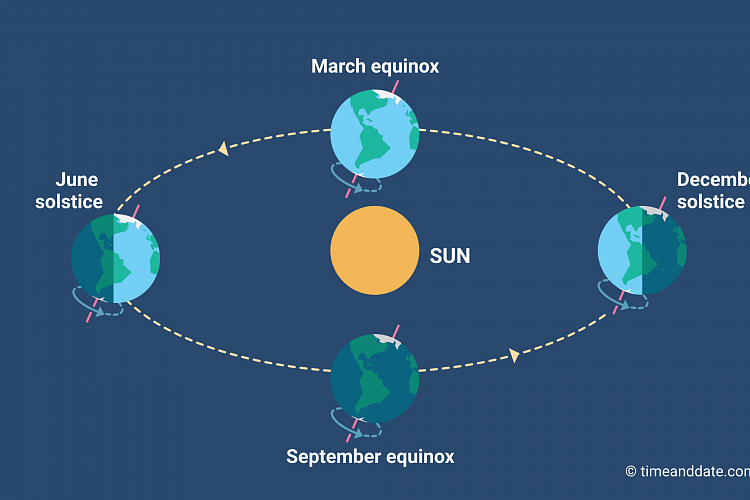
Equinoxes and solstices are points in contrast on either side of the equator, and the March equinox or spring / vernal equinox of the northern hemisphere is the autumnal /fall equinox of the southern hemisphere. The equinoxes are by definition those days in which night and dare are nearly 12 hours long all over the world. Hence the word equinox which means equal night in Latin. Keep in mind however that the equinoxes are not a time of exactly 12 hours daylight or 12 hours night, instead, the equinox is based on the earth's tilt and that time when the Earth is neither tilted toward or away from the Sun but is perpendicular to the rays of the Sun.
The equinox is not exactly the same as the day when period of daytime and night are of equal length for two reasons. Sunrise, which begins daytime, occurs when the top of the Sund's disk rises above the eastern horizon. At that time, the disk's center is still below the horizon. Secondly, Earth's atmosphere refracts sunlight. As a result, an observer sees daylight before the first glimpse of the Sun's disk above the horizon. To avoid this ambiguity, the word equilux is sometimes used to mean a day on which the periods of daylight and night are equal.Times of sunset and sunrise vary with an observer's location by longitude or latitude.
An Equinox may occur on any planet with a significant tilt to its rotational axis. Most dramatic of these is Saturn, where the equinox places its ring system edge-on facing the Sun. As a result, they are visible only as a thin line when seen from Earth. When seen from above – a view seen by humans during an equinox for the first time from the Cassini space probe in 2009 – they receive little sunshine and more "planetshine."
This lack of sunshine occurs once every 14.7 years. It can last a few weeks before and after the exact equinox. The most recent exact equinox for Saturn was on 11 August 2009. Its next equinox will take place on 30 April 2024.
One effect of equinoctial periods is the temporary disruption of communications satellites.Geostationary satellites in particular are susceptible there are a few days around the equinox when the sun goes directly behind the satellite relative to Earth (i.e. within the beam-width of the ground station antenna) for a short period each day. The Sun's immense power and broad radiation spectrum overload the Earth station's reception circuits with noise and, depending on antenna size and other factors, temporarily disrupt or degrade the circuit. The duration of those effects varies but can range from a few minutes to an hour depending on the frequency band since a larger antenna has a narrower beamwidth and hence experiences shorter duration "Sun outage" windows.)
No comments:
Post a Comment